Do search engines index all your content to rank in the SERP? How confident are you about the correct indexing of your webpage? There are many reasons why your page may not be indexed, which hampers its visibility. That’s why it is essential to know about common page indexing issues and how to solve them.
You may face page indenting issues due to inappropriate use of noindex meta, robots.txt, canonical tags, errors like- redirect issues, 3XX, 4XX, 5XX, XML sitemaps issues, and more. In this article, we have listed all these common issues your web pages may face during indexing. You will also learn the ways to solve these problems and rank your website higher in the search engine. So, without any further delay, let’s begin-
What Is Page Indexing Issue?
Page indexing issues indicate the difficulties search engines face in crawling and including web pages in their search index. However, before knowing about page indexing issues, you must first know what page indexing is.
Page indexing is also known as web page indexing. It is a process by which search engines like Google or Yahoo collect, analyze, and store information from web pages in their databases. The search engine adds all relevant information to its database while indexing any web page.
The indexing elements include the page’s content, keywords, metadata, and other relevant information. So, when a user browses any queries, the search engine matches the indexed information from the page and displays the result accordingly. But page indexing issues arise when the search engine faces problems in including web pages in their search index.
Page indexing issues can occur for several reasons. Some of the major reasons include-
- Too new website takes time to index
- No domain name inclusion
- Recent redesigning or rebranding of the website
- Website missing sitemap
- Poor website structure
- Not mobile-friendly web design
- Not connecting pages to rest of the sites; orphan pages
- Not following ADA compliance for building websites
- Low-quality content on the website
- Suspicious or hard-to-read code
- Google penalty receiving
Effect of Page Indexing Issues On Your Website
Page indexing issues have a direct impact on your website. It drops the reach and overall performance of your website. The effect of page indexing issues are as follows-
- Reduced Organic Traffic
Search engines cannot display your site to the user if you have page indexing issues. This will hinder access to your website resulting in a drop in user reach and engagement. Thus, you will lose organic traffic to your website.
- Poor Search Engine Rankings
Pages that are not indexed properly show poor search engine ranking. They may not even appear to search ranks at all. This will badly affect your visibility and public reach. Besides, finding your content will be harder for the potential audience.
- Bad User Experience
A visitor gets frustrated when he lands on a non-indexed or error page. It shows blank pages or broken s, leading to a poor user experience. This results in higher bounce rates and lower engagement metrics. Thus, improper indexing negatively impacts your website’s overall performance.
- Inefficient Crawling and Indexing
The search engine uses a lot of time while indexing complex content. This ends up in inefficient use of their crawling budget. So, when you upload new or updated content, its indexing is delayed. Thus, the latest content of your page is not indexed on time, losing potential opportunities for ranking.
- Lost Revenue and Conversions
Does your website depend on organic traffic for selling products? If yes, then you are the worst sufferers of page indexing issues. Indexing issues will drop public reach, directly impacting your business. Fewer visitors mean fewer conversions of visitors to customers, which means a drop in sales.
- Penalties From Search Engines
Search engines take page indexing issues seriously. So, if they find frequent technical or indexing issues, your website may get a penalty that will badly impact the site. These penalties may include-
- Lower rankings for relevant keywords
- Trigger algorithmic penalties
- Complete removal of the website from the search engine’s index
Covering up penalties from search engines is very challenging. Even if you solve the issues with page indexing, revising the penalties takes a lot of time. At this time, your website gets into the bottom line.
12 Common Page Indexing Issues And Its Solution
The most common issues that you may face due to page indexing issues are as follows-
Noindex Meta Tag Issues
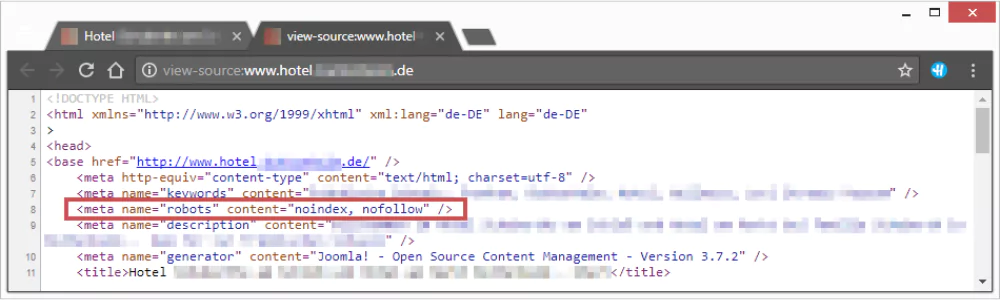
The “noindex” meta tag is used for blocking specific pages of your website. For instance, if you don’t want to give public access to certain pages, you can add this tag to the HTML code. When search engines find this tag in your coding, they don’t add the page to their index. But when this tag is misused or placed on any essential page, it instructs search engines not to index it. As a result, the page is not shown in the search list, and so the visitor will not find the content in the Google SERP.
Solution:
If your website page has “noindex” indexing issues, here are the ways to solve it-
- Perform a comprehensive audit of your website’s meta tags to identify pages that have the “noindex” directive.
- Remove the “noindex” meta tag from the HTML code from inappropriate pages.
- If you are using a content management system (CMS) or SEO plugins, review the settings to fix “noindex’.
Robots.txt Blocking Issues
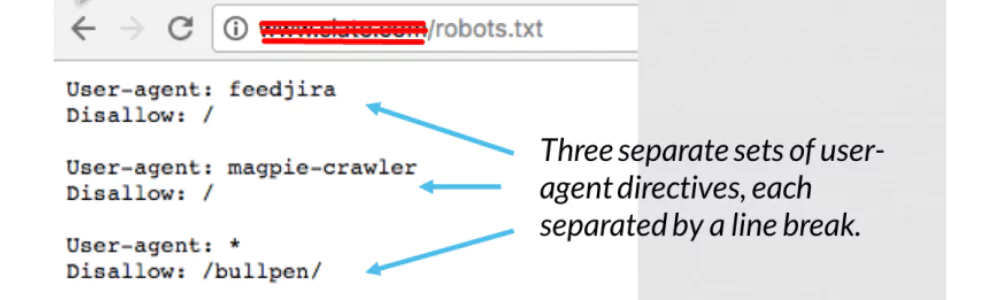
Robot.text blocking is used to instruct the search engine/bot to prevent crawling to specific parts of your website or certain URLs by using the robots.txt file. It is a simple text file placed in the root level of a website’s page containing instructions for web bots on what to or not to index/crawl.
But when this is used in an improper way, it can block indexing essential contents, which creates page indexing issues. Besides blocking essential pages, it may also bring other indexing issues like-
- Partial or incomplete indexing
- Delayed indexing of new content
- Blocks crawling in essential CSS or JavaScript files
- Indexing private or confidential information
For these reasons, the search engine fails to index your content which restricts SERP visibility.
Solution:
Follow the below steps to get rid of the robots.txt blocking issues of page indexing:
- Review the current robots.txt file on your website. Make sure it is correctly formatted and doesn’t contain any restraining rules.
- Use tools like Google Search Console’s “robots.txt Tester” or third-party SEO tools to find specific URLs that are on the block.
- Update the robot.text file and remove the restraining rules to allow search engines to index/crawl.
- After fixing the robot.text blocking issues, update your sitemap, and submit it to search engines. You can use Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools for this process.
Content Issues

The content is the heart of a website. Poor content can damage search engine crawling, affecting page indexing. Here are some common content issues related to page indexing-
- Duplicate Content
Google bots or other web crawlers are not so perfect for detecting the contents’ authenticity accurately. Your website may get into duplication claims unintentionally. The search engine gets confused when similar content is found in different URLs of the same website. They can’t decide which one to take under indexing since it can’t index multiple copies from the same page. So, it cuts out the repetitive content, considering them as duplicates.
You might be creating duplicating content without realizing it. This is very common, especially for large business platforms. For example- if you use a product description identical or very close to other websites, it will be termed as duplicate content. This happens mostly to multilingual websites. As a result, the search engine will not index your website. So, when visitors browse for the same product, content from your web page will not appear.
Solution:
Follow the below guidelines to save your content from duplication tags-
- Give your best to create unique content
- Experiment with the outline of your content to help differentiate
- Be careful in handling URL parameters and pagination settings.
- Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of duplicate content.
- If URL variation is the cause of your content duplication, set up 301 redirects to the preferable version.
- Thin Content
Google or other search engine bots take thin content as low-quality content as they can’t add too much value to the user. These contents are too short in length ( less than 300 words) and lack detail or valuable information. This is why search engines skip them while indexing. So, if you have thin content on your website pages, they are at a prominent risk of not being indexed.
Solution:
- Delete the thin contents
- Move the essential elements of the thin content to other similar content
- Always create comprehensive and in-depth blog posts of at least 1500 – 2500 words.
- Fresh Content
Google SERP takes time to rank your content. So, when you upload new content, don’t hope for immediate ranking. It can take one week to a few months to index your page. Therefore, give the search engine time to index your page. Besides, the web pages that don’t update their content lose indexing tendency. It is a good practice to maintain and update your uploaded content to bring better outcomes.
Solution:
- Be patient and wait a few months to get your new content indexed by search engines.
- Keep existing content up-to-date by revisiting and refreshing it
- Encourage users to increase website engagement by commenting, liking, and sharing to keep the page active
- Indexed Without Content
One of the common problems in page indexing is crawling empty pages or pages without any content. It harms your website more than not indexing issues. When such empty or contents with no actual information get indexed, it gives the visitor a bad user experience. This increases the bounce rate, which affects your Google ranking. The search engine takes your page as poor or low-quality content and drops its ranking.
Solution:
- Add useful content to the indexed page
- Use the robots.txt file to prevent search engines from indexing pages
Redirect Error: 3XX Errors

Redirects or redirection are useful when you want to direct users and search engine crawlers from one URL to another. For instance, you can use this if your page is moved to a new location or when multiple URLs need to be combined into one. Thus, it will automatically send visitors and search engine crawlers from one URL to another URL.
But the issues occur when the redirect is implemented incorrectly. This sends the wrong HTTP status codes to search engine crawlers, which causes unintended problems with indexing. SEOs often make mistakes in placing the redirects correctly that end up in errors. This may be due to using too long a redirect chain or an empty URL. These mistakes bring redirect errors of different types; for example-
- 301 Moved Permanently Issues
- 302 Found (Temporary Redirect) Issues
- 307 Temporary Redirect Issues
When these types of errors are found on pages, they redirect the page to an irrelevant or non-existent URL. This eventually makes it difficult for the search engine to understand the direction or index the original location of the page.
Solution:
- Use 301 permanent redirects for permanent URL changes and 302 temporary redirects for temporary changes.
- Avoid creating loops by directing URLs in an infinite loop.
- Don’t exceed the max length for redirect URL (2 MB for Google Chrome)
- Avoid using long redirect chains that misuse the crawling budget.
- Ensure not having any 404 or 410 URLs in the chain.
- Always redirect URLs to relevant pages.
Client Errors: 4XX Errors

Client Errors or 4XX refers to the server issues caused by the client. Here by the client, it indicates the web browser, search engine crawler, or user. If the request by the client has any issues when they try to access any webpage, it sends back a 4XX error. As a result, search engine crawling is affected, which hampers page indexing. Such errors can pop up at your disposal due to different reasons. Here are the most common client error you will find-
- 401: Unauthorized Error
Error 401 indicates unauthorized access that needs access approval. When you put restrictions on certain web pages, it shows 401 or an unauthorized error. As the search engine tries crawling these pages, they end up showing a 401 HTTP status code. If you put this code intentionally, then it’s ok to preserve sensitive content. But in case the code is inserted by mistake, it will prevent your page from indexing.
Solution:
- Remove the authorization request
- Grant access permission to search engine
- 403: Forbidden Error
When you provide login, password, and other credentials to enter the page but don’t give access permission, it shows a 403/forbidden error. This case is seen where a user attempts to access restricted website areas without proper authorization. So, when the Google bot goes to the page for indexing, it shows an error without getting access to the page. This code is used to maintain privacy for certain parts of the content. But if the page gets blocked by mistake and you need to index it follow the below solution-
Solution:
- Allow access for the non-signed-in user
- Permit Googlebot to enter the page to analyze and index it
- 404: Page Not Found Error
404 or page not found error is the most common issue with page indexing. The server may show this error due to several reasons. For example- you made a mistake when writing the URL, deleted the URL but left the page on the sitemap, etc. As a result, when search engine crawlers index your website, it encounters multiple 404 errors. Their capacity to crawl and find new or updated content is thus hindered, leading to incomplete indexing. This leaves some pages unindexed or out of the database.
Solution:
- Make sure the URL is properly written and update the sitemap.
- Set a 301 redirect if you have moved the URL to a new page.
- If you have deleted the page, remove it from the sitemap and set 404. This will save the crawl budget by preventing Google from crawling to the page.
- Soft 404 Issues
Soft 404 errors occur when a page returns a “200 OK” status code indicating that the page exists. But actually, the page’s content is found empty or does not provide useful information to users. These pages may not directly return a “404 Not Found” response code, but they still act as soft 404s since they fail to deliver the requested content. Your page may face this issue for several reasons. For example- keeping the content too short, missing JavaScript files, page cloaking, broken connection to the database, etc.
Solution:
- Set up a 301 redirect if the page is moved to a new address.
- Remove the content from the sitemap after marking it as 404 if the content is deleted.
- If you want to keep the page indexed, ensure it contains valuable and meaningful content. Check that all scripts and elements on the page are correctly rendered, and there are no issues with blocked resources.
- If soft 404 errors occur due to server issues, make sure your server is working correctly. Then you can request the search engine for a re-indexing.
Server Errors: 5XX Errors

Server Errors or 5XX errors are HTTP status codes indicating server-side issues. When a user browses the web page, the error returns to inform the client that it encountered a problem in fulfilling the request. This may occur when the server cannot process the request properly, or something unexpected happens on the server’s end. The issues of server errors include-
- 500: Internal Server Error
- 501: Not Implemented Error
- 502: Bad Gateway Error
- 503: Service Unavailable Error
- 505: HTTP Version Not Supported
When search engine crawlers face these errors on your website, it fails to continue the crawling process. As a result, some pages of your website don’t get indexed. This directly hampers the search engine ranking.
Solution:
- Check the affected URL using Google Search Console (GSC)
- Reduce the server load for dynamic page requests.
- Regularly monitor your website’s hosting server. This will ensure your website is not misconfigured, down, or overloaded.
- Ensure your website is not blocking Google bots from crawling.
After fixing these issues, apply for reindexing requests to Google.
XML Sitemap Errors
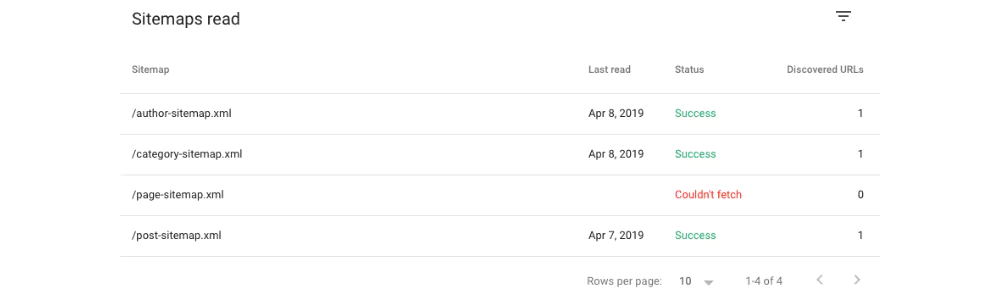
XML sitemap is a file used to collect information about each URL of the website to assist in search engine indexing. It consists of a list of URLs, their latest update, the importance of one URL compared to relative URLs, etc. Using these elements helps the search engine to understand the content and its structure to help index accordingly.
The issues occur when there is an error in the XML sitemap. It confuses the bots in understanding the structure and collecting information from the content. As a result, your web pages are not identified by search engines or are led to index the wrong URLs. This eventually hampers the indexing of new content and hinders visibility in search engine results.
Solution:
- Include all relevant and important pages on your website in an XML sitemap.
- Fix any syntax or formatting issues in your XML sitemap. You can use online XML sitemap validators to check for these errors.
- Update XML sitemap regularly and remove outdated ones as needed.
Orphaned Pages
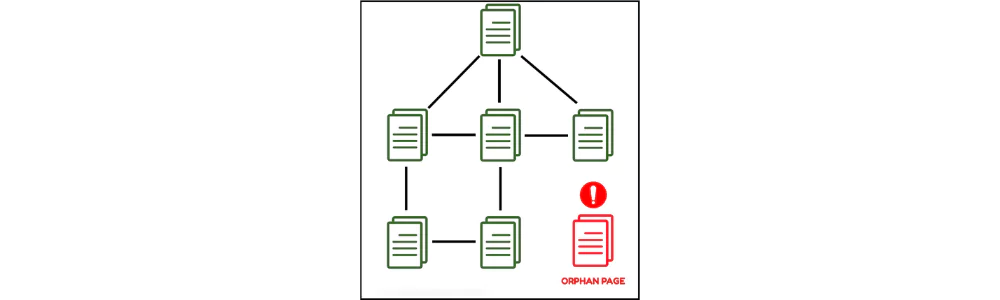
Orphan pages are those pages of the website that have no internal or external ing within the website. In other words, these pages aren’t connected to any other pages on the website. So, there aren’t many chances to direct people or search engine crawlers to them. Orphan pages, thus, have no alternative ways to get indexed.
Solution:
- Conduct a thorough audit of your website to identify orphaned pages. Mark the important and relevant pages to implement ing.
- Include orphaned pages in your website’s XML sitemap.
Crawl Errors: Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
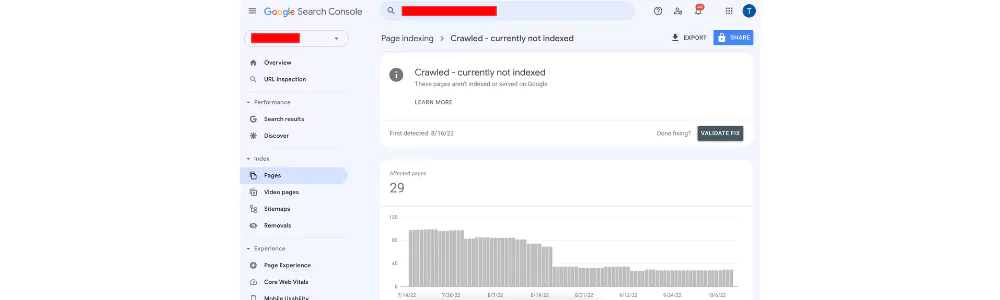
You may find a “Currently Not Indexed” message from the Google server engine when the bot crawls your page, but due to some reason, it decided not to index it. The page is in a wait for indexing, and Googlebot may index it later until there is no not-indexing direction.
Google’s crawling and indexing process is multi-step, and not all crawled pages are indexed right away. It ranks pages based on various criteria, including page quality, relevancy, and freshness. So, this process takes time, for which Google may send you a crawl error. However, there might be some major issues rather than just inspection timing. For example- the crawl mirror may occur due to duplicate content, thin content, Noindex Tag, robots.txt file, canonical tag, etc.
Solution:
In most cases, you won’t need to request reindexing because it is waiting, and Google is aware of that. The crawling and indexing engines will eventually index the page. Yet, you can check for any errors or instructions for resisting page indexing.
DNS Resolution Errors
DNS stands for ‘Domain Name System.’ It translates the human-readable domain names to computer-accepted IP addresses to help the internet connect the devices. But when (DNS) fails to resolve the domain name of a website to its corresponding IP address, it shows a domain resolution error. As a result, when the search engine reaches the DNS, it finds no IP addresses; and so can’t locate the information. Thus, it fails to index your web page. This may be due to many reasons, for example-
- Incorrect DNS configuration
- DNS propagation delay due to updating nameservers or modifying DNS records
- Problems with the domain registration, expiration, or ownership
- Temporary issues or outages with the DNS servers
- Network connectivity problems
Solution:
- Check the DNS setup of your website to confirm that the DNS records are correct and up to date.
- Reduce the quantity of DNS lookups by using fewer third-party services.
- Solving these issues, request for a re-indexing.
Server Timeout

When the server takes too long to respond to the search engine crawling, it shows a server timeout. This means the connection between the crawler and server failed, which interrupted the page indexing.
Solution:
- Implement server-side caching to store and serve frequently requested pages more quickly.
- Ensure that your server is well-configured and has enough resources to handle incoming requests efficiently.
To optimize your website to prevent such issues, check out this article- WordPress Website Optimization Techniques.
Canonicalization Issues
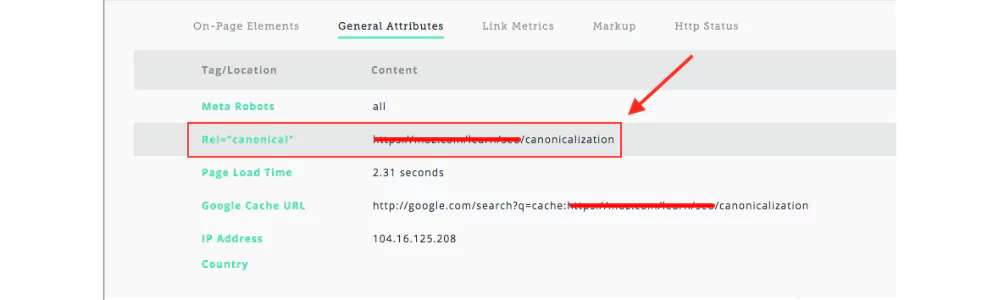
Canonical tags are used when there are multiple URLs for the same or similar version of the same content. This tag is used to select specific content for Google/ search engines for indexing. If you want to avoid content duplication issues, using canonical tags is essential. But when there are canonicalization issues, it causes problems in page indexing. Some major issues with its solution are as follows-
- Incorrect Canonical Tags
If your canonical tag is not correct, Google chooses the version of the page by itself. This may result in selecting low-quality content for indexing.
Solution:
- Check your URLs manually
- Use the site audit features of software like Ahrefs or Semrush to put canonical tags correctly.
- Google Chose Different Canonical Than User
Sometimes you put a canonical tag on a specific page, but Google chooses to index some other version of the page. As a result, your desired page with more precious information doesn’t get indexed. This can also confuse the search engine in the future.
Solution:
- Put a canonical tag on the page chosen by Google.
- But if you want to give priority to your chosen page for canonical tags, redirect the Google chosen page to your desired URL.
- Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag
Google doesn’t index the pages that are duplicates of the canonical tagged pages. This is not a problem until and unless your canonical tagged page is properly indexed.
Solution:
You need not take any action for this as the canonical tagged page with a better version of the content is already indexed.
How To Identify Page Indexing Issues?
From the above segment, you know about different page indexing issues. But how to know which issue your website is facing? To remedy the problem, first, you need to identify it. So, here are the ways of identifying page indexing issues on your website-
- Google Search Console
Google Search Console, also known as Google Webmaster Tools, is a free application by Google that helps to monitor the search engine’s performance, including page indexing. It offers you an Index Coverage Report that helps you to identify any prevalent page indexing issues. This report includes-
- Valid pages that are indexed successfully.
- Pages with errors that prevent indexing (e.g., crawl errors, server errors).
- Pages that are excluded from indexing (e.g., noindex tags, canonicalization issues)
- Pages with warnings or issues that need attention.
With these directions, you can learn about the indexing statute of your page. This will help to take the necessary steps to resolve these issues and improve the indexation of your website’s content.
- Site Auditing Tools
Google Search Console is a great tool, but it only displays problems when Google attempts to index a website and fails for any reason. If such a page is not even detected by Google, GSC will have no idea about the indexing problem. To solve this issue, you should have access to site auditing tools. These tools crawl your website, analyze its structure, and provide detailed reports on various SEO aspects and indexing issues. Some famous site auditing tools are as follows-
The Bottom Line
Page indexing is crucial in keeping your website active and ranking in Google SERP or other search engines. Due to issues with page indexing, you will lose the organic traffic of your website, which hampers your business.
To avoid this, make sure to use restriction tags like- robots.txt and noindex meta tags, maintain the quality of the content, use best SEO practices, and keep your page optimized. Thus, your page will get indexed properly and increase its visibility in Google SERP.
Continue Reading:
Responsive Or Adaptive Web Design?